Hereditary Mixed Polyposis Syndrome
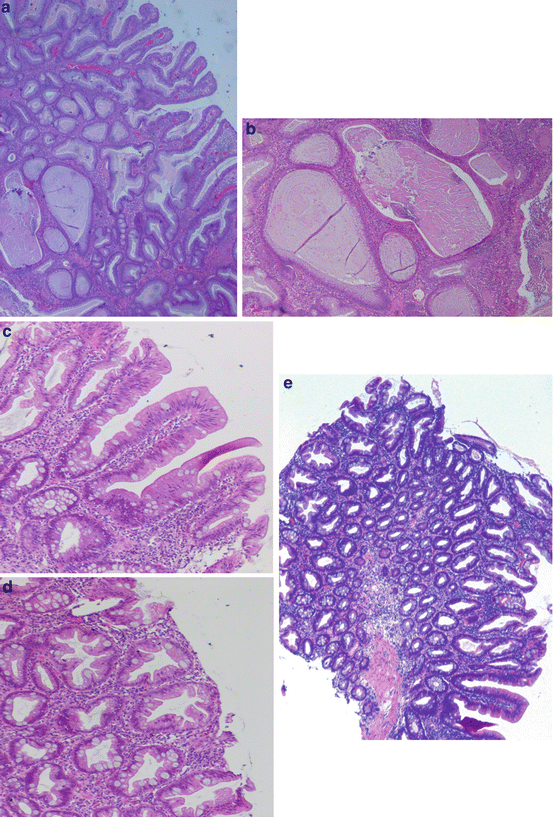
Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome. Syndrome CS serrated hyperplastic polyposis syndrome hereditary pancreatic cancer and hereditary gastric cancer. The hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome HMPS is characterized by atypical juvenile polyps colonic adenomas and colorectal carcinomas CRC. Foreach of these syndromes we outline diagnostic criteria and indications.
Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome. GREM1 Duplication The GREM1 gene leads to hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome characterized by multiple polyps of mixed pathology and high risks for colorectal cancer. Please call 0800 783 4372 between 9am and 5pm or e-mail palsnwlhnhsuk.
Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome. HMPS A cancer family syndrome characterized by the development of a variety of different types of polyps in the colon including atypical juvenile polyps and adenomas of the colon and by the development of colorectal carcinoma cancer of colon and rectum. Hereditary Mixed Polyposis Syndrome First published July 2012 Review date July 2014 Reference 162012 PALS is a confidential service for people who would like information help or advice about the services provided by any of our hospitals.
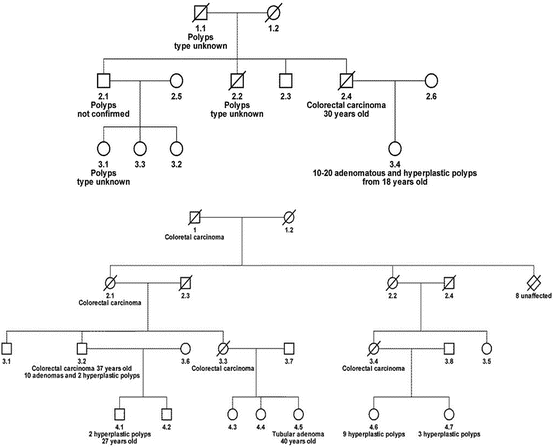
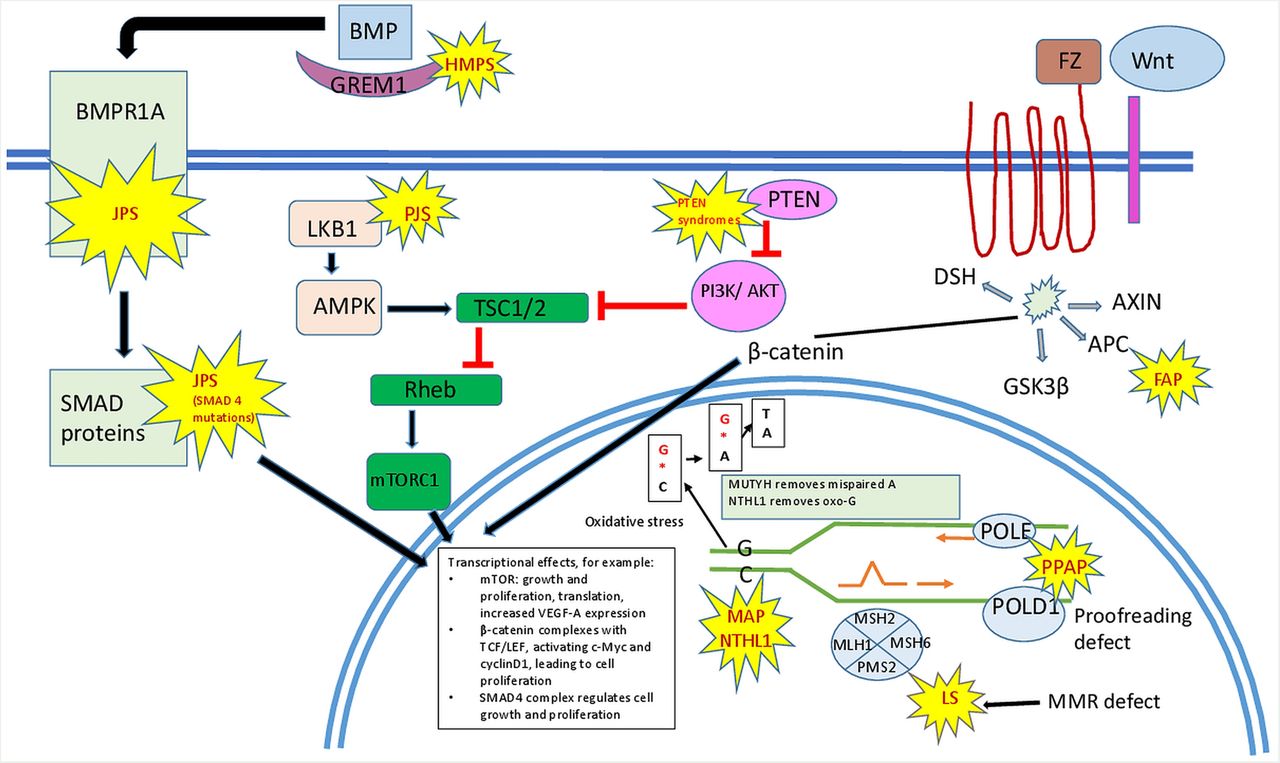
The hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome HMPS is characterized by atypical juvenile polyps colonic adenomas and colorectal carcinomas CRC. Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome HMPS is characterized by apparent autosomal dominant inheritance of multiple types of colorectal polyp with colorectal carcinoma occurring in a high proportion of affected individuals. Genetic Heterogeneity of Hereditary Mixed Polyposis HMPS2 610069 is caused by mutation in the BMPR1A gene 601299 on.
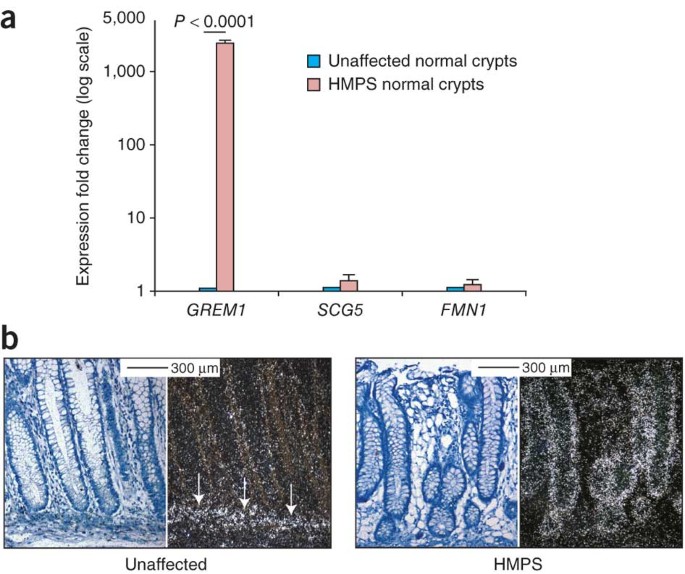
Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome HMPS is characterized by apparent autosomal dominant inheritance of multiple types of colorectal polyp with. Adenomas are most frequent type. Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome is a rare colon cancer predisposition syndrome caused by a duplication of a noncoding sequence near the gremlin 1 DAN family BMP antagonist gene GREM1 originally described in Ashkenazi Jews.
Individuals with HMPS are predisposed to multiple types of. Few families with GREM1 duplications have been described so there are many questions about detection and management. The hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome HMPS is characterized by atypical juvenile polyps colonic adenomas and colorectal carcinomas CRC.
A large duplication upstream of GREM1 is associated with hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome HMPS. HMPS is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
A large duplication upstream of GREM1 is associated with hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome HMPS.
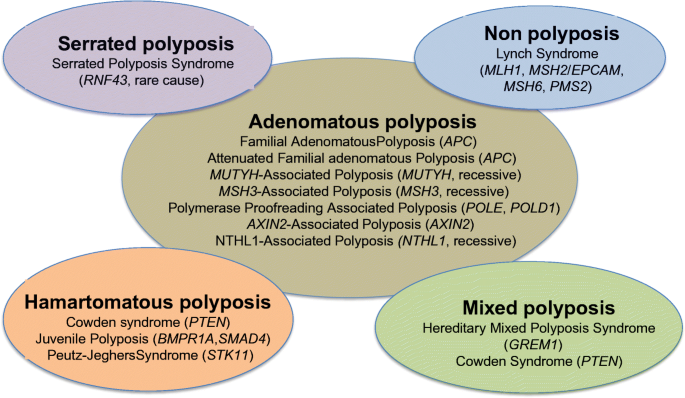
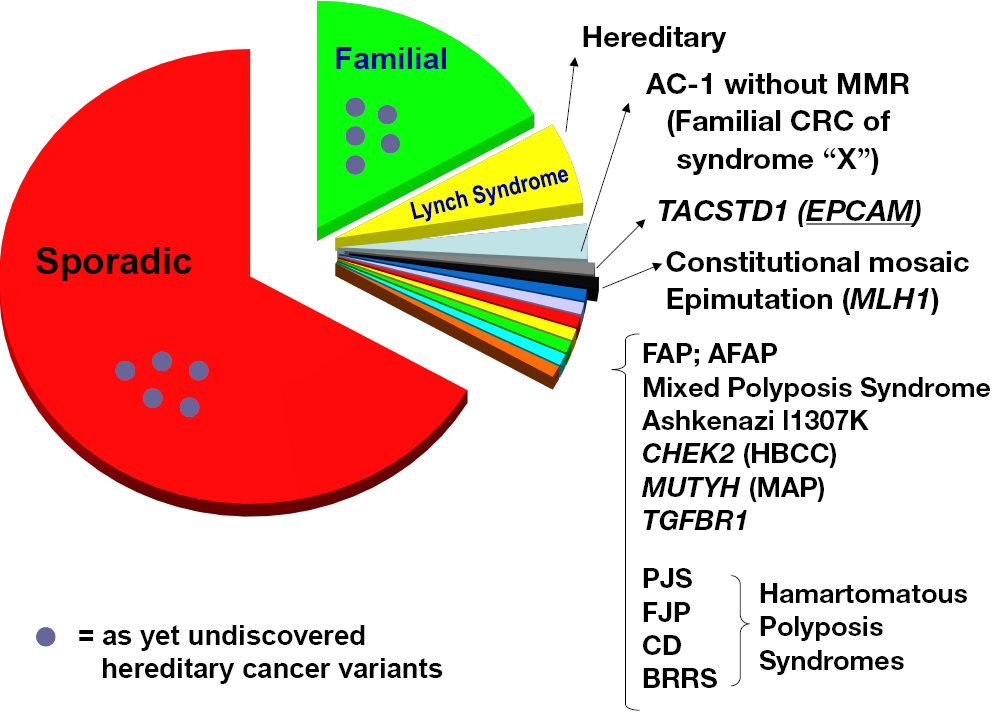
Adenomas are most frequent type. The hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome HMPS is characterized by atypical juvenile polyps colonic adenomas and colorectal carcinomas CRC. Familial adenomatous polyposis FAP leads to the growth of hundreds to thousands of non-cancerous benign polyps in the colon and rectum. Hereditary syndrome characterized by the appearance of various types of polyps many of which are mixed in pattern. Genetic Heterogeneity of Hereditary Mixed Polyposis HMPS2 610069 is caused by mutation in the BMPR1A gene 601299 on. For genetic evaluation describe the currently knownassociated underlying genes and make. Foreach of these syndromes we outline diagnostic criteria and indications. A polyp is a growth of normal tissue that forms a lump. As the name suggests a variety of polyps.
GREM1 Duplication The GREM1 gene leads to hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome characterized by multiple polyps of mixed pathology and high risks for colorectal cancer. Genetic Heterogeneity of Hereditary Mixed Polyposis HMPS2 610069 is caused by mutation in the BMPR1A gene 601299 on. Hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome. Hereditary Mixed Polyposis Syndrome First published July 2012 Review date July 2014 Reference 162012 PALS is a confidential service for people who would like information help or advice about the services provided by any of our hospitals. Genetic Heterogeneity of Hereditary Mixed Polyposis HMPS2 610069 is caused by mutation in the BMPR1A gene 601299 on. Symptoms of FAP may include dental abnormalities tumors of the connective tissue desmoid tumors and benign and malignant. A number sign is used with this entry because of evidence that hereditary mixed polyposis syndrome-2 HMPS2 is caused by heterozygous mutation in the BMPR1A 601299 gene on chromosome 10q23.









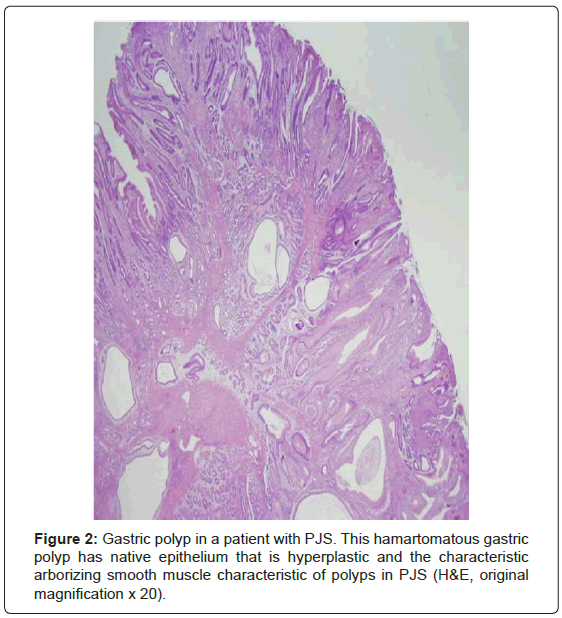




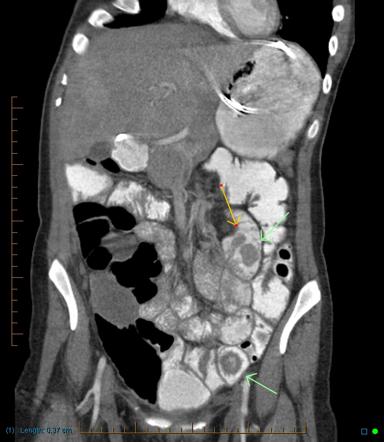
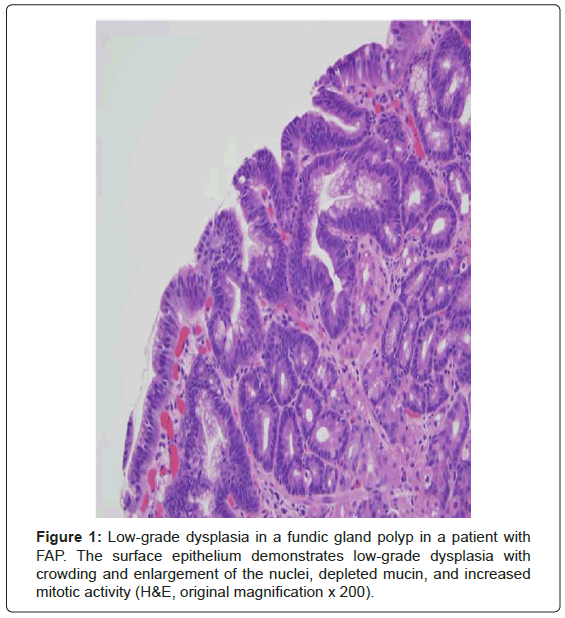




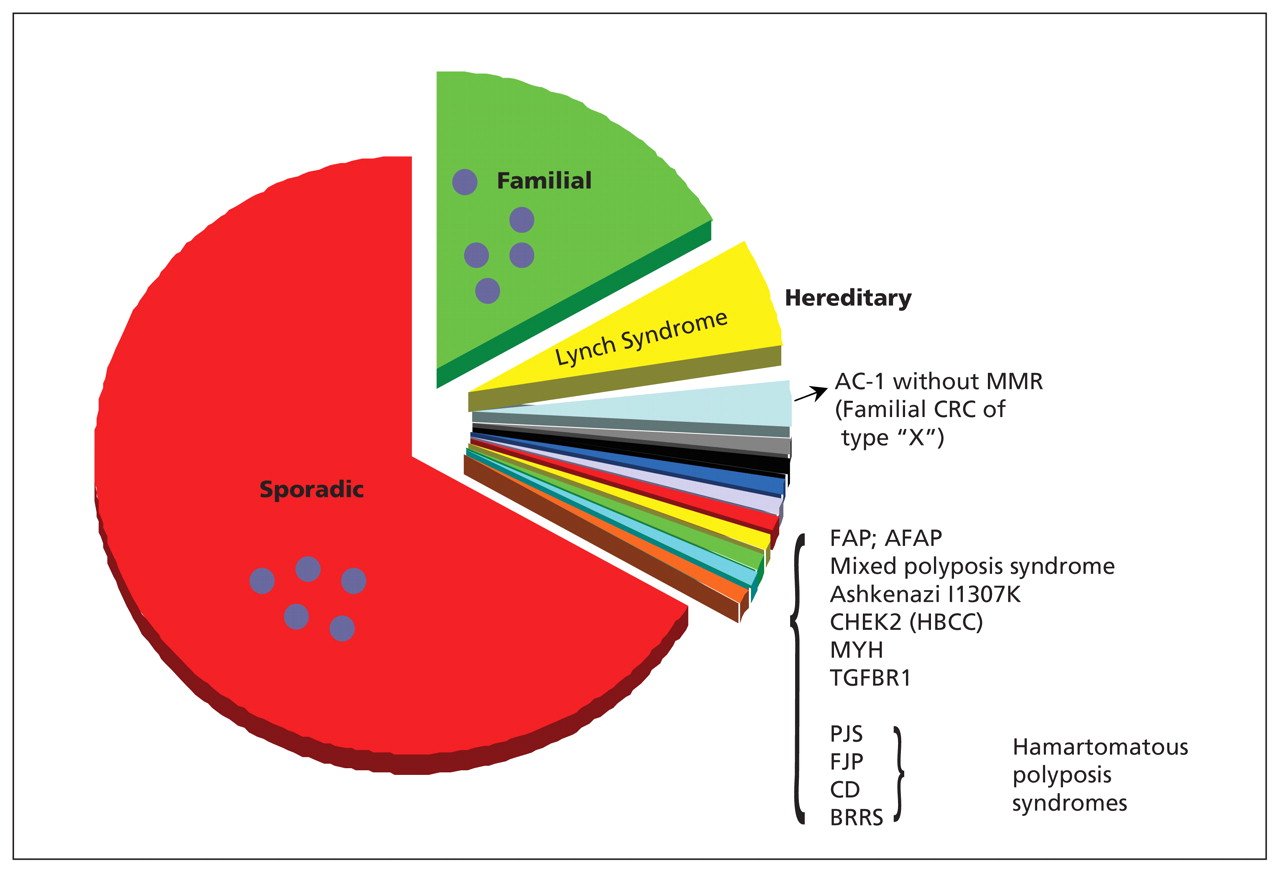


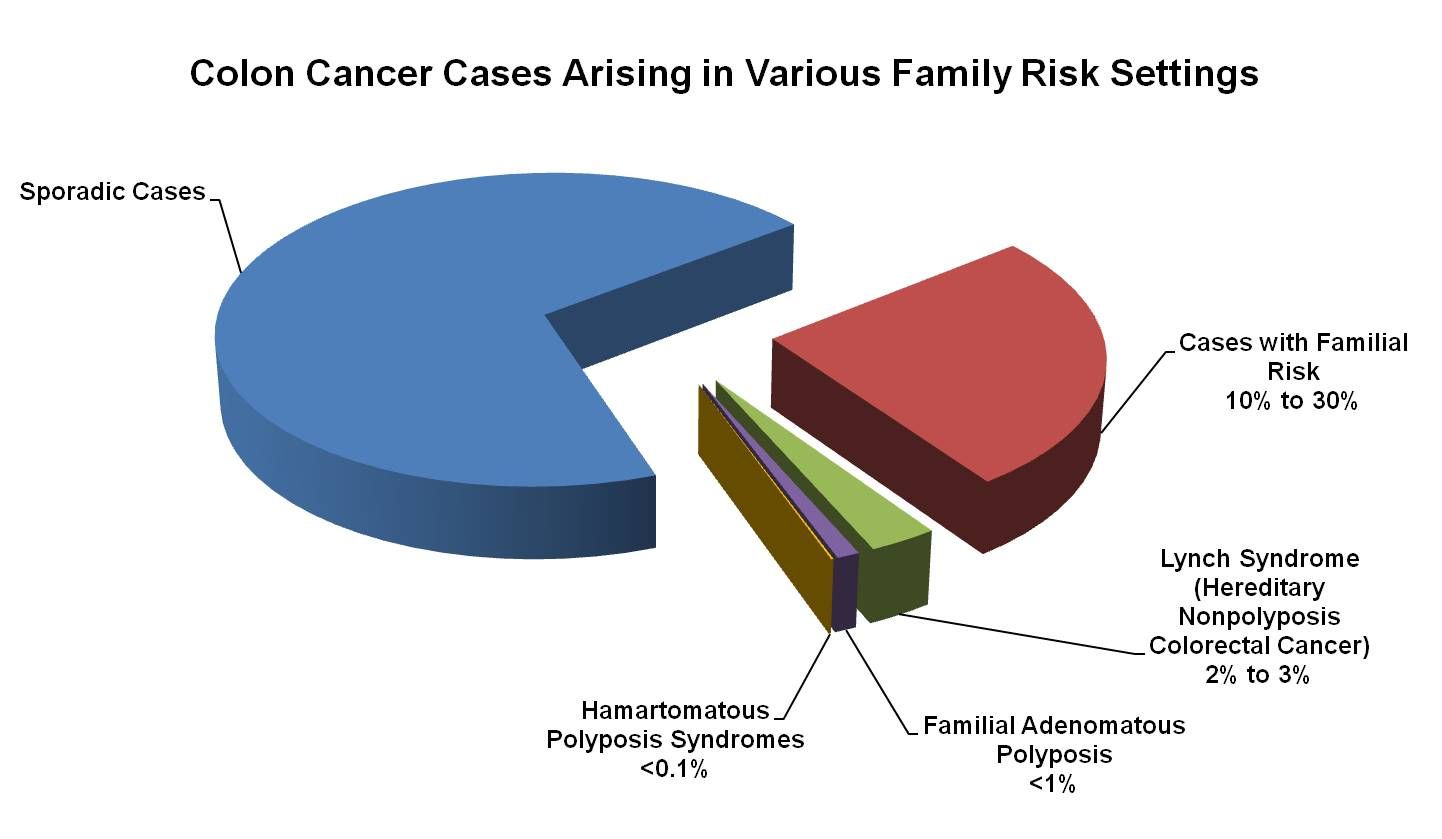


Post a Comment for "Hereditary Mixed Polyposis Syndrome"