Chronic Granulomatous Disease Of Childhood
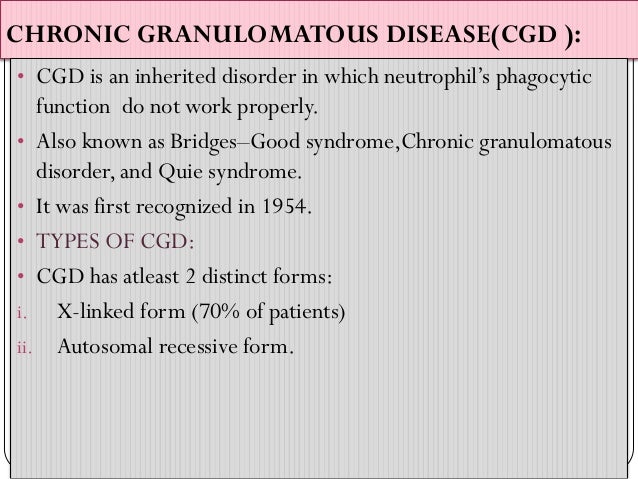
Chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. Granulomatous Disease Chroniccomplications Granulomatous Disease Chronicpathology. Chronic granulomatous disease is an hereditary disease of males who have an abnormality in their defense against bacterial infections. The pathobiology of chronic granulomatous disease CGD of childhood a heterogeneous phenotypic disorder characterized by chronic and recurrent infection has become more completely understood over the past three decades.
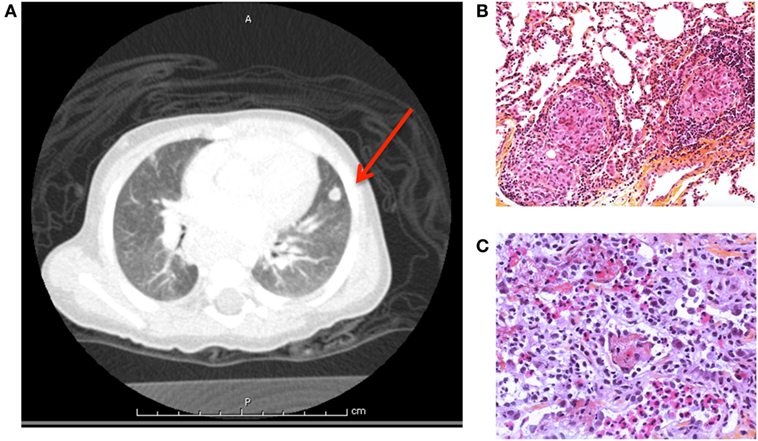
An unusual cause of honeycomb lung. We have followed nine male patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease at The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto since 1972. Chronic granulomatous disease of childhood.
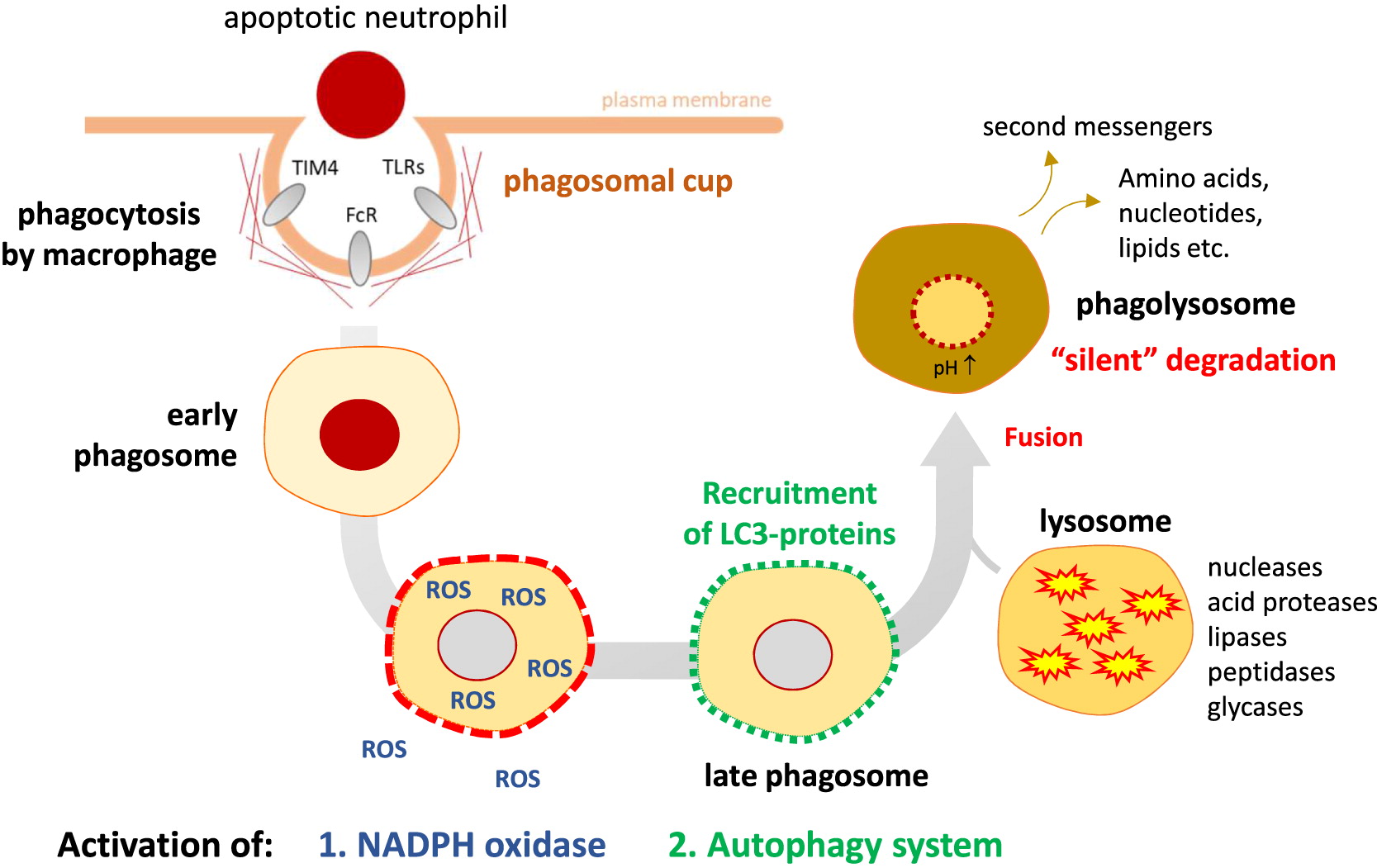
Microbial ingestion and phagosome formation are normal. Chronic granulomatous disease CGD is a rare congenital immunodeficiency that affects 1. Recently it has been shown that granulocytic leukocytes in th.
Chronic Granulomatous Disease is one of the classic primary immunodeficiencies of childhood. Rarely are other organs affected. Histopathological features of chronic granulomatous disease CGD in childhood Chronic granulomatous disease may present to histopathologists in a wide range of tissue specimens most often demonstrating features of active chronic inflammation with or without granuloma formation.
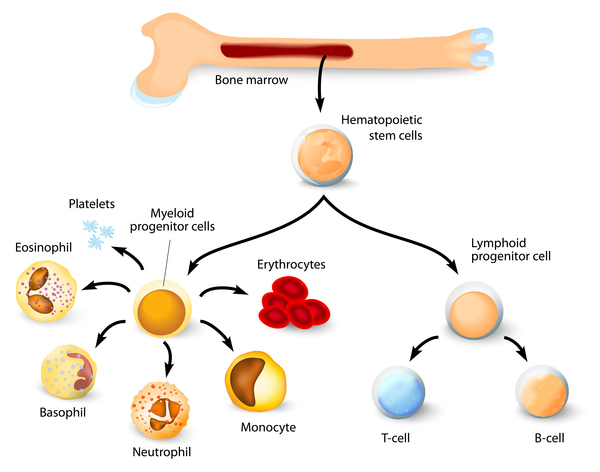
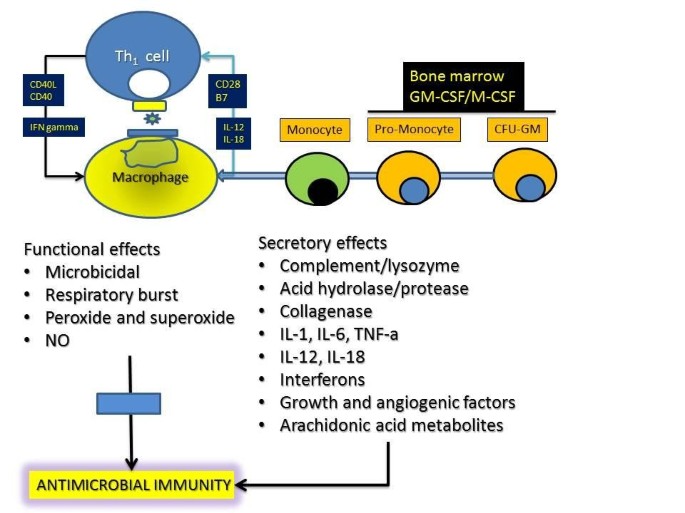
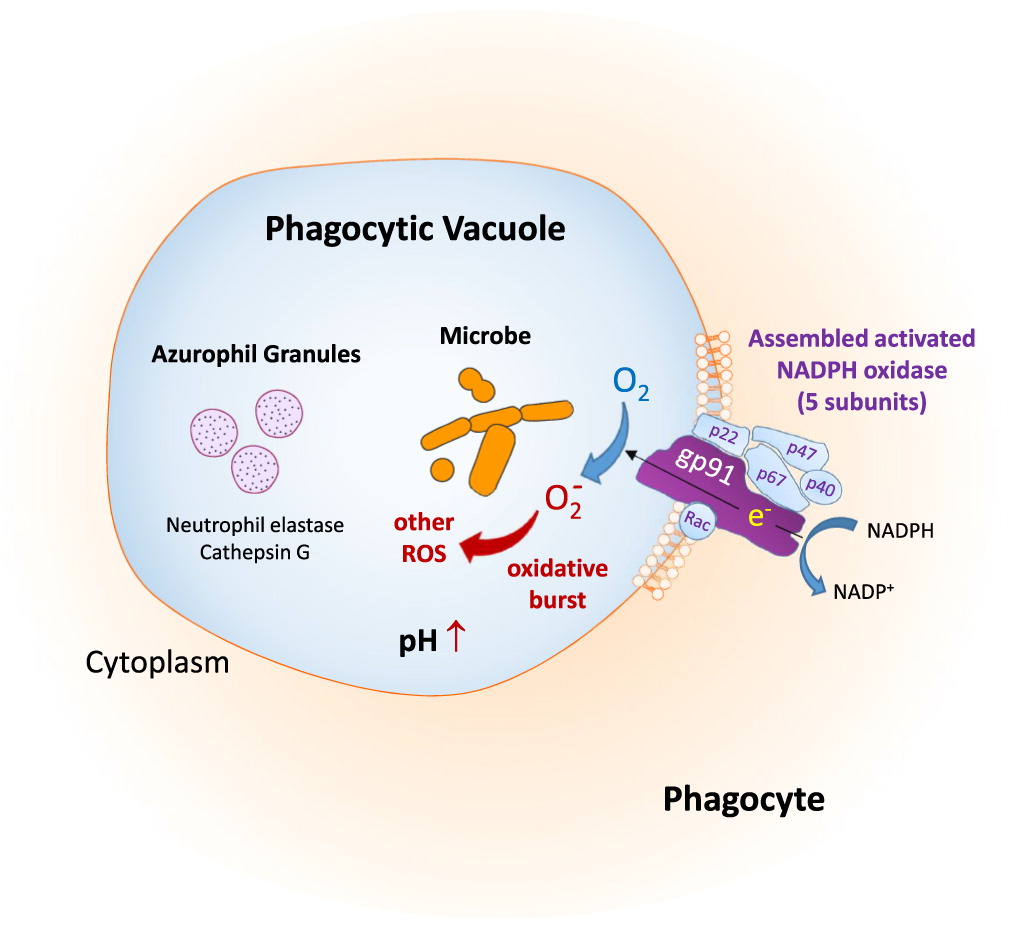
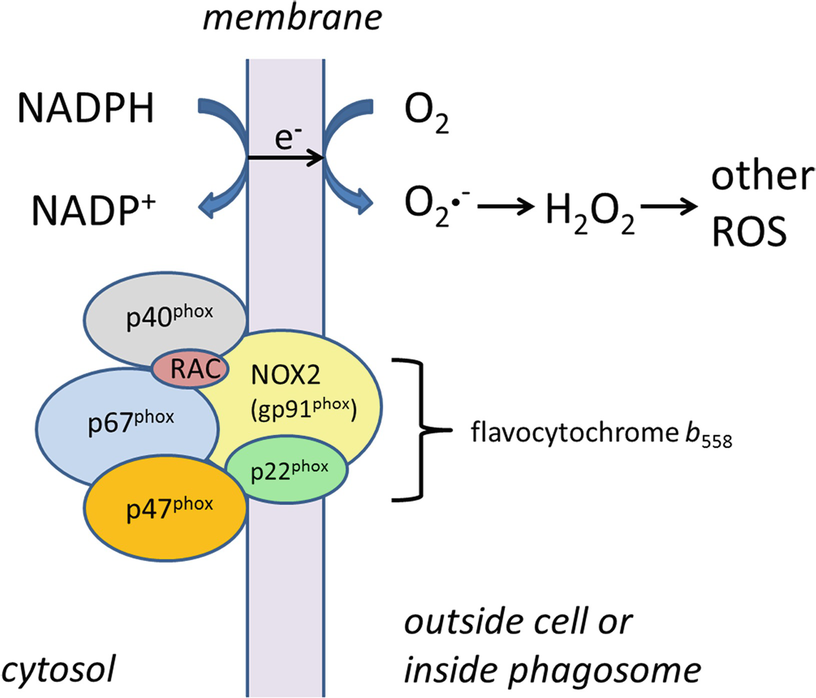
Chronic granulomatous disease CGD of childhood is a rare inherited disease in which phagocytic cells fail to produce the normal respiratory burst in response to infectious stimuli leaving the patient particularly susceptible to infections with bacteria and fungi that produce catalase. All 3 exhibited normal cellular and humoral immunity normal neutrophil phagocytic ability and defective neutrophil bacterial capacity. While the incidence and severity of bacterial and fungal infections have been greatly reduced in this patient population much remains to be learned about the pathophysiology of the disease particularly for autoinflammatory manifestations.
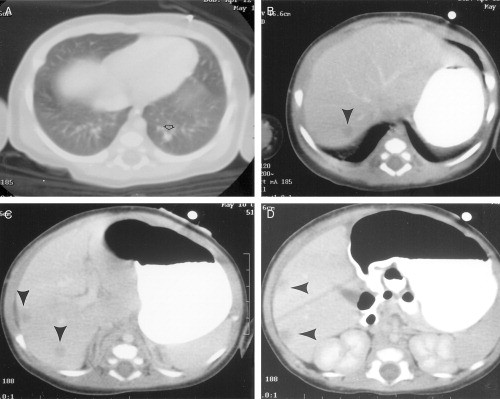
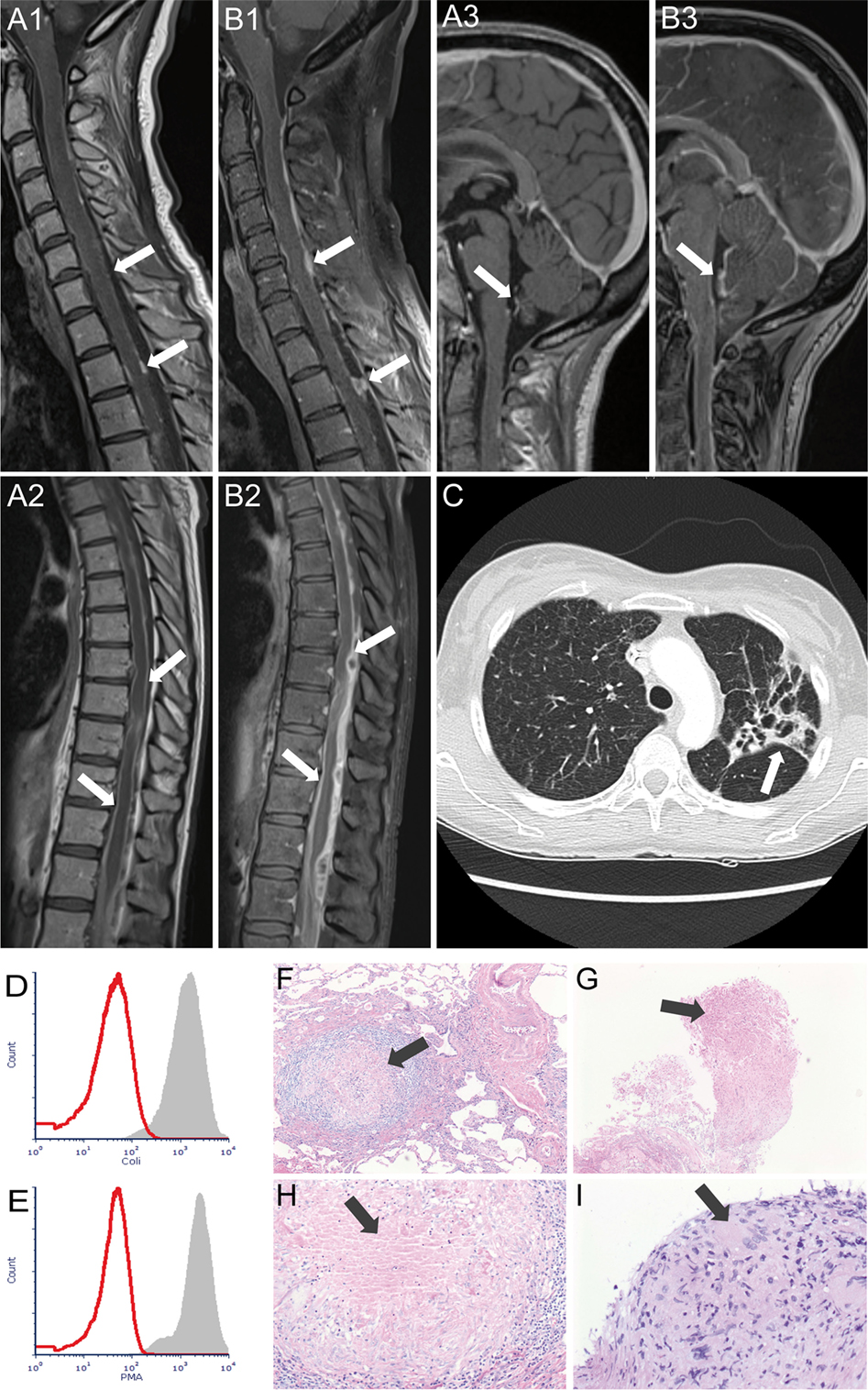
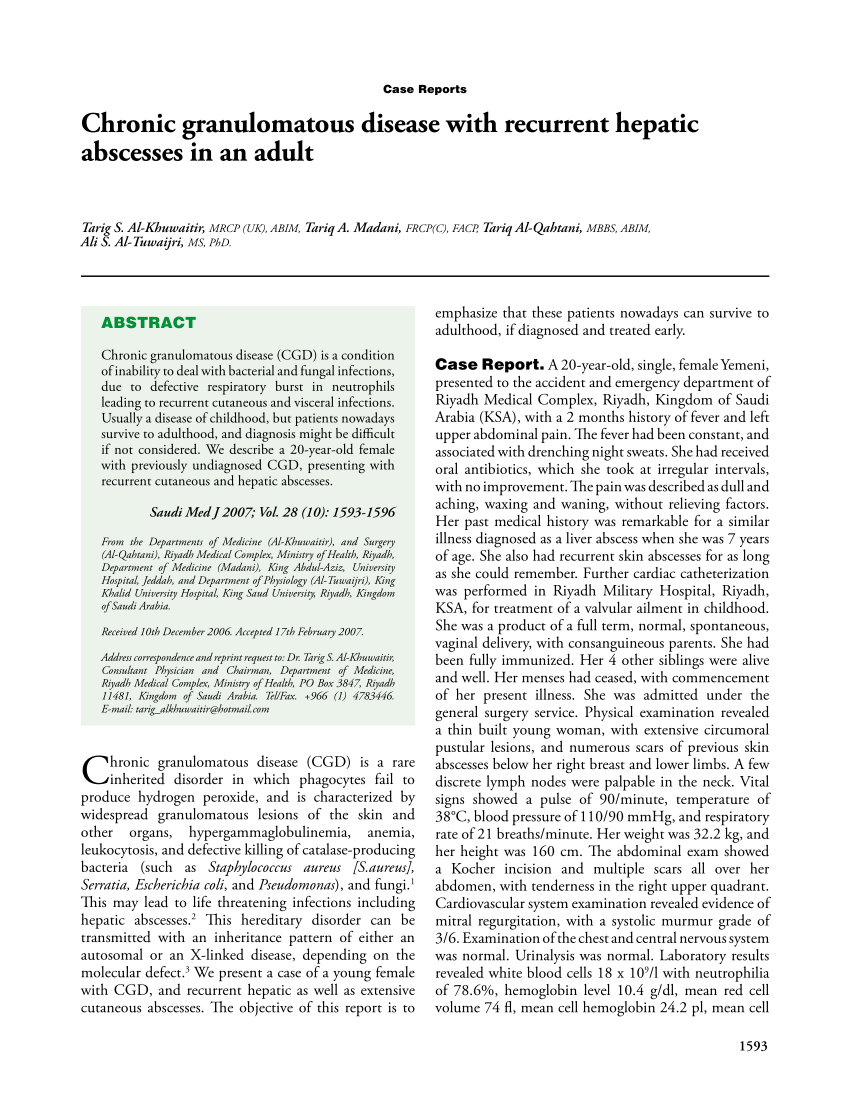
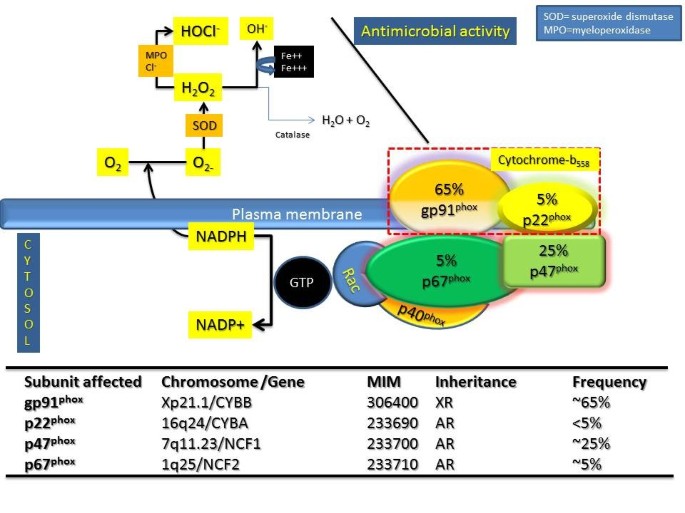
Chronic granulomatous disease in children is a disease of recurrent sepsis in children which results from a deficiency of a white cell DPNH oxidase. Chronic granulomatous disease CGD of childhood is a rare entity. The most common sites of involvement are the lungs lymph nodes skin liver spleen and bones.
Chronic granulomatous disease in children is a disease of recurrent sepsis in children which results from a deficiency of a white cell DPNH oxidase. 250000 of the population which is characterized by recurrent bacterial and fungal infections and by.
6750550 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types.
All 3 exhibited normal cellular and humoral immunity normal neutrophil phagocytic ability and defective neutrophil bacterial capacity. Granulomatous Disease Chroniccomplications Granulomatous Disease Chronicpathology. Hartenberg MA Kodroff MB. 1192868 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types. The most common sites of involvement are the lungs lymph nodes skin liver spleen and bones. CHRONIC GRANULOMATOUS DISEASE OF CHILDHOOD ByWJHCALDICOrFMB BSt and RLBAEHNER MD4 BOSTONMASSACHUSETTS CHRONIC granulomatous disease isa fatal hereditary disease inwhich there are recurrent and chronic bacterial infec-tions ofthe skin respiratory tract lymph nodes liver spleen and bones due to diminished bacterial killing byleukocytes. The pathobiology of chronic granulomatous disease CGD of childhood a heterogeneous phenotypic disorder characterized by chronic and recurrent infection has become more completely understood over the past three decades. Chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. Chronic granulomatous disease in children is a disease of recurrent sepsis in children which results from a deficiency of a white cell DPNH oxidase.
We have followed nine male patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease at The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto since 1972. The disease is characterized by recurrent infections with granuloma and abscess formation caused by an inherited defective neutrophil leukocyte function. The most common sites of involvement are the lungs lymph nodes skin liver spleen and bones. The fatality of the disease has previously been emphasized. An unusual cause of honeycomb lung. Chronic granulomatous disease of childhood is an inherited metabolic disorder of the leukocyte series characterized by impaired intracellular microbicidal activity. Frayha HH Biggar WD.































Post a Comment for "Chronic Granulomatous Disease Of Childhood"